Human Eye and the Colourful World
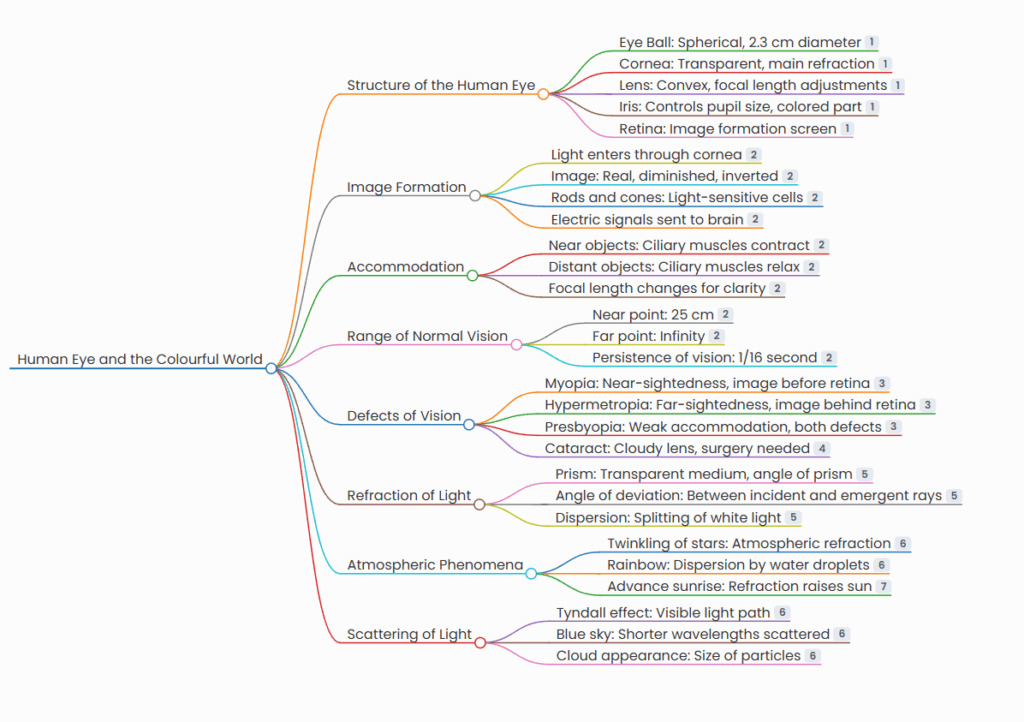
Structure of the Human Eye
- Eye Ball: Spherical, 2.3 cm diameter
- Cornea: Transparent, main refraction
- Lens: Convex, focal length adjustments
- Iris: Controls pupil size, colored part
- Retina: Image formation screen
Image Formation
- Light enters through cornea
- Image: Real, diminished, inverted
- Rods and cones: Light-sensitive cells
- Electric signals sent to brain
Accommodation
- Near objects: Ciliary muscles contract
- Distant objects: Ciliary muscles relax
- Focal length changes for clarity
Range of Normal Vision
- Near point: 25 cm
- Far point: Infinity
- Persistence of vision: 1/16 second
Defects of Vision
- Myopia: Near-sightedness, image before retina
- Hypermetropia: Far-sightedness, image behind retina
- Presbyopia: Weak accommodation, both defects
- Cataract: Cloudy lens, surgery needed
Refraction of Light
- Prism: Transparent medium, angle of prism
- Angle of deviation: Between incident and emergent rays
- Dispersion: Splitting of white light
Atmospheric Phenomena
- Twinkling of stars: Atmospheric refraction
- Rainbow: Dispersion by water droplets
- Advance sunrise: Refraction raises sun
Scattering of Light
- Tyndall effect: Visible light path
- Blue sky: Shorter wavelengths scattered
- Cloud appearance: Size of particles